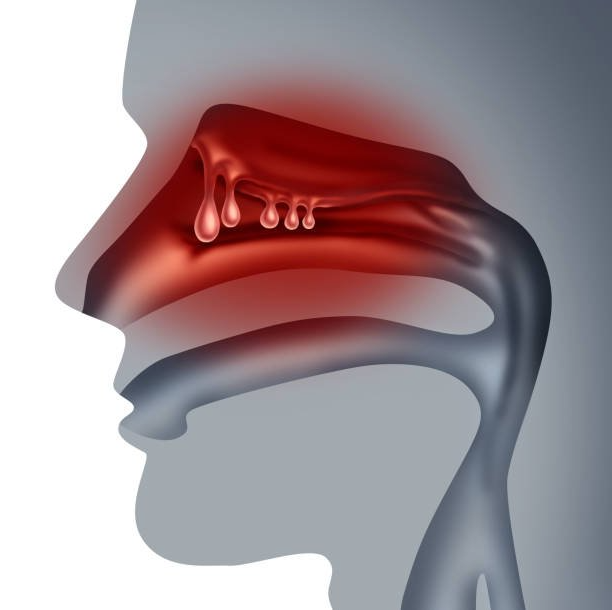
Sinusitis
When your sinuses are inflamed, blocked, or filled with fluid, it can lead to discomfort and symptoms similar to a cold or an allergy.
Treatments aim to improve symptoms of sinusitis by reducing inflammation and removing infection.
Types of Sinusitis
Sinusitis has different names depending on the length of symptoms.
Acute Sinusitis
This is when you experience a sudden onset of symptoms that don’t go away after 10 days. This type of sinusitis usually responds well to antibiotics. Repeated episodes of acute sinusitis are termed recurrent acute sinusitis.
Chronic Sinusitis
The symptoms or chronic sinusitis include nasal congestion, drainage, facial pain or pressure, and a loss of smell for more than 12 weeks consecutively.
Treatment for Sinusitis
A sinus infection (or sinusitis) is an inflammation or swelling of the sinus tissues, which keep the nose clean and free of bacteria. While anyone can have sinusitis, people with nasal allergies, nasal polyps, or asthma are more susceptible. Depending on the severity of the infection, treatment may range from allergy medication to antibiotics to surgery.